MAY IS EDS AWARENESS MONTH!
Archives
What is Ehlers- Danlos Syndrome?
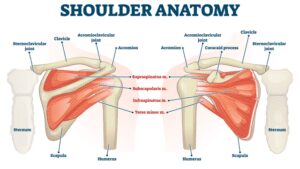
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a genetically inherited connective tissue disorder in which a gene mutation impacts the normal production of collagen in the body. Collagen is the most prevalent protein in the body primarily composing tendons, ligaments, fascia, and cartilage. It comprises the architectural framework for the body’s structural support system and is found in all organ systems including the digestive tract, cardiovascular system, urinary system, neurological system, and musculoskeletal system. This means that EDS can potentially impact all body systems, but not all presentations are the same.
There are 13 subtypes of EDS depending on patient presentation. There may be symptom overlap between the subtypes. The 3 most common types are the autosomal dominant types meaning there is a 50% chance that parents with the disorder will pass this along to their children. These 3 types are the classical type which primarily impacts the skin, the vascular type which primarily impacts the blood vessels, and the hypermobility type which primarily impacts the ligaments, fascia, and tendons surrounding the joints. All EDS types except for the hypermobility type have a specific gene mutation that has been identified which a geneticist can accurately test to diagnose the EDS type properly. The hypermobility EDS is the only type that does not have a gene identified as the primary cause of the disorder and must be diagnosed clinically using specific international criteria recently revised in 2017 including the Beighton Scale and Brighton scales.
The most common EDS type that we treat at BEAT Physical Therapy is the hypermobility type. Common musculoskeletal complaints include severe joint pain, muscle spasming, myofascial trigger points, frequent subluxations or dislocations of joints, cartilage or tendon tears, and falls or balance problems.
Some common co-morbidities with EDS include Chiari Malformation, Tethered Cord Syndrome, Postural Orthostatic Tachycardic Syndrome (POTS), Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), Cranio-cervical Instability (CCI), aneurysms, Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP), Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Raynaud’s syndrome, migraines, fibromyalgia, Gastroparesis and digestive motility issues, prolapsed organs, and neuropathies. Poor wound healing and excessive scarring and bruising are common as well.
There is no known cure for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, but customized physical therapy can help in providing pain relief, joint stabilization, and improved quality of life and functional capacity for individuals with this disorder. These PT treatments can include trigger point dry needling, myofascial release for the spasming muscles, muscle energy techniques to keep joints in alignment, core and joint stabilization exercises, bracing, balance exercises to improve proprioceptive capacity, and taping techniques for pain relief and stabilization of joints.
For more information, the Ehlers-Danlos Society provides excellent resources and information regarding this disorder. https://www.ehlers-danlos.com/eds-types/
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collagen